The Big Picture
LLMs can autonomously discover, call, and chain live services exposed as agent actions to complete real tasks without fine-tuning, using a flexible multi-agent platform and zero-shot prompting.
ON THIS PAGE
Key Findings
SAGE connects a language model to a running multi-agent platform so the model can pick the right service, call it, ingest the result, and continue — all at runtime. Multiple prompting strategies trade off speed, correctness, and cost: a single-module loop is simple and often effective, while multi-tool workflows split planning, construction, and evaluation for harder requests. Benchmarks used simulated office, warehouse, and music services to show the system can handle both single-tool and multi-tool workflows and work with both hosted and self-hosted models.
Avoid common pitfallsLearn what failures to watch for
Data Highlights
1Benchmark environment: 3 agent containers, 15 agents, and 102 actions used to simulate real-world services and stateful operations.
2Prompts split into single-tool (1 required call) and multi-tool (>=2 required calls) scenarios to test simple vs. chained workflows.
3Simple single-module method makes one tool call per loop iteration; experiments ran LLM modules using gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18 for the evaluations.
What This Means
Engineers building AI assistants that must interact with internal services (email, databases, devices) will find a blueprint for exposing those services as callable actions and letting models orchestrate them. Technical leaders evaluating production agent setups can use the demonstrated methods to compare simplicity versus staged orchestration for correctness, cost, and speed trade-offs.
Key Figures
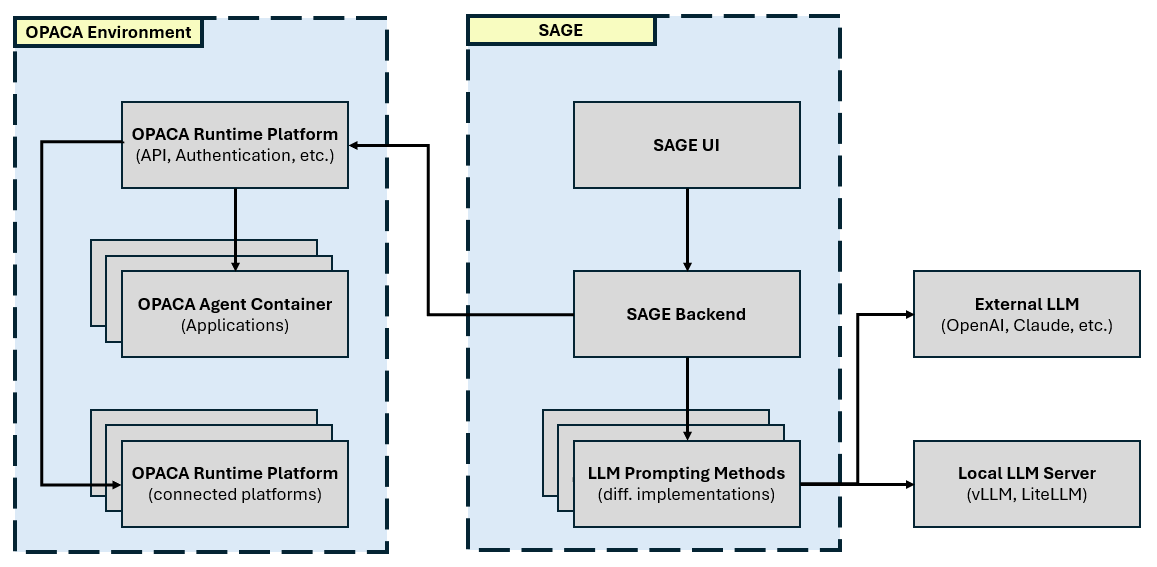
Fig 1: Figure 1: SAGE System Architecture

Fig 2: Figure 2: Screenshot of SAGE, showing ‘agents’ panel and empty chat window with example prompts.
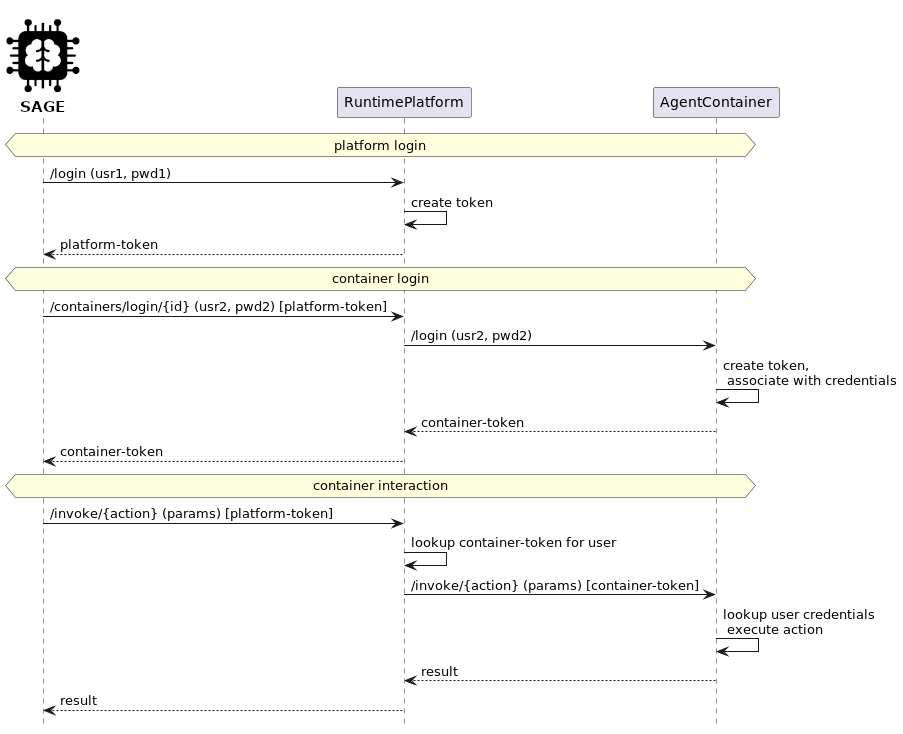
Fig 3: Figure 3: Authentication to Runtime Platform and Agent Container
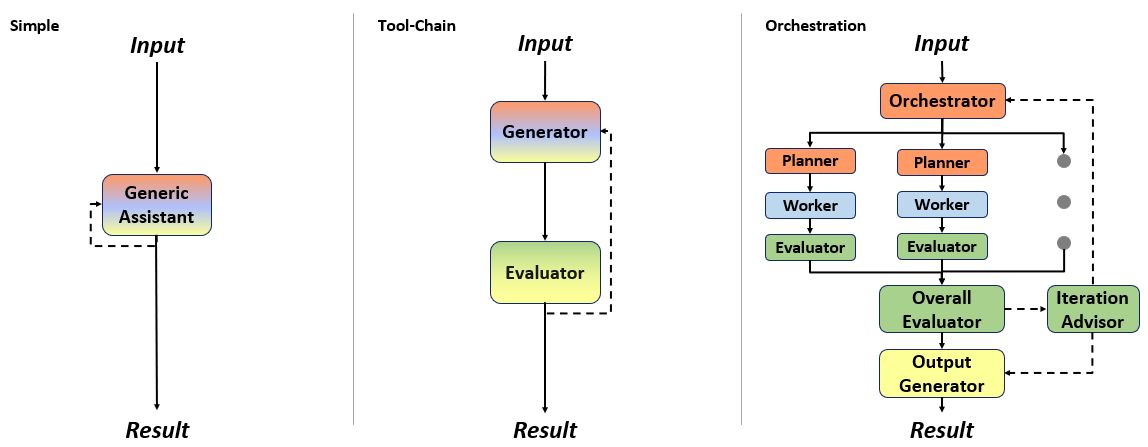
Fig 4: Figure 4: Overview of the Method Architectures implementing the different modules of the Tool Generation Process in 4.2 in their LLM modules. (Red: Planning , Blue: Construction , Green: Evaluation , Yellow: Output Generation .)
Ready to evaluate your AI agents?
Learn how ReputAgent helps teams build trustworthy AI through systematic evaluation.
Learn MoreConsiderations
The benchmarks run on simulated containers created by the authors, so real-world latency, security constraints, and unexpected API behavior were not fully evaluated. The malformed outputs can occur with the single-module method, and it is limited to one tool call per loop, which can prematurely stop complex flows. Evaluation relies on curated prompts and a judge model, so results may differ on open-ended user inputs or in noisy production environments.
Deep Dive
SAGE is a runtime that plugs a language model into a multi-agent microservice platform so the model can call available services (called actions) as tools at inference time. The system exposes agent actions via a unified API, injects the tool descriptions into model prompts at runtime, and automatically executes any valid tool call the model emits, feeding results back into subsequent model iterations. It supports multiple models (hosted or self-hosted via proxies), streaming responses, file inputs, and several prompting strategies that vary how the thinking, tool formulation, and evaluation steps are split across model modules. Three main methods three main methods were implemented: a Simple single-module loop that repeatedly asks one model to pick and call tools; a two-module tool-chain that separates generation and evaluation; and a multi-stage orchestration approach that divides the user request into subtasks based on agent composition. The team evaluated SAGE with three purpose-built containers (office, warehouse, music) containing 15 agents and 102 actions and ran curated single-tool and multi-tool prompts. Results show the approach is practical and extendable: the Simple method works well with strong models but can fail on formatting and is limited to one call per iteration, while orchestration helps for complex, multi-step tasks. The system is presented as a reusable foundation for integrating internal services into LLM-driven workflows, with planned future additions for proactive scheduling and introspection.
Need expert guidance?We can help implement this
Credibility Assessment:
Authors have low h-indices and no strong institutional signals; arXiv preprint.