The Big Picture
Adaptive selection of roles, pairwise collaboration styles, and model assignments cuts token use by about 11–16% and raises accuracy by ~1.5–3.3% across five standard benchmarks.
ON THIS PAGE
The Evidence
Constructing AI teams by (1) picking only the roles needed for a query, (2) choosing explicit pairwise collaboration strategies (like debate or critique) between those roles, and (3) assigning cheaper or stronger models per role leads to a more cost-efficient system. Jointly optimizing which agents to include, how they interact, and which models they run outperforms state-of-the-art single-model or per-agent routing approaches. The approach keeps execution simple by using a directed acyclic graph of agents so runs terminate predictably. Results show consistent token savings and modest but reliable accuracy gains across knowledge, math, and coding tasks. This aligns with Consensus-Based Decision Pattern.
Not sure where to start?Get personalized recommendations
Data Highlights
111.17%–16.35% reduction in token consumption compared to prior state-of-the-art methods
21.46%–3.34% relative improvement in accuracy across evaluated benchmarks
3Validated across 5 benchmarks: MMLU, GSM8K, MATH, HumanEval, and MBPP
What This Means
Engineers building production AI agents who need to balance cloud cost and answer quality can use these ideas to pick cheaper models for some roles while keeping overall performance. Technical leads evaluating architectures for multi-agent workflows can adopt edge-level (pairwise) collaboration patterns to squeeze cost savings without losing accuracy. Researchers working on agent collaboration should note that modeling pairwise strategies explicitly unlocks gains beyond per-agent routing.
Key Figures
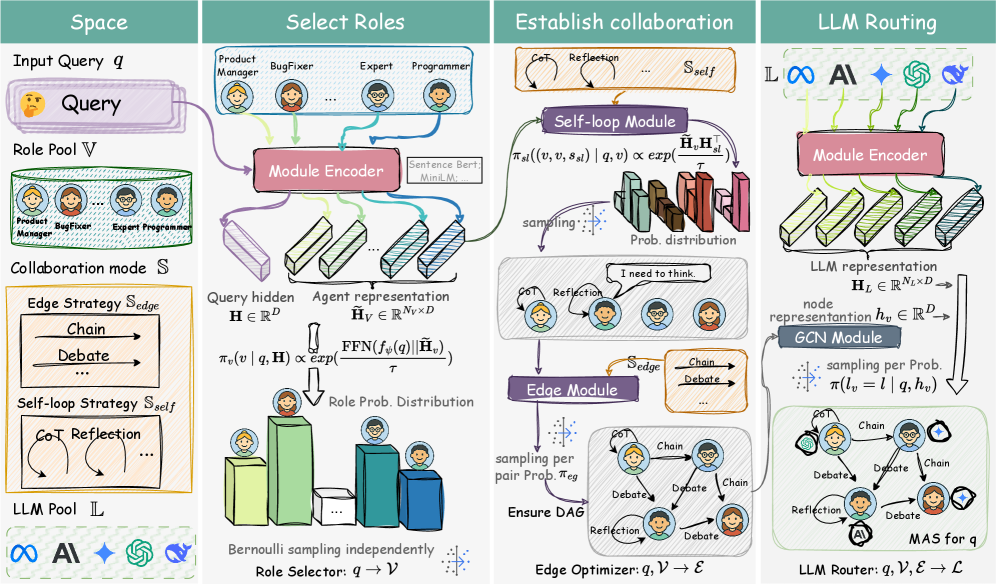
Fig 1: Figure 1: The overall framework of our proposed SC-MAS . The roles for accomplishing the query are first selected from the candidate pool, followed by establishing the collaboration relationships between these selected roles, and finally assigning the appropriate LLMs, thus generating an executable graph representation of the heterogeneous collaboration strategies MAS.
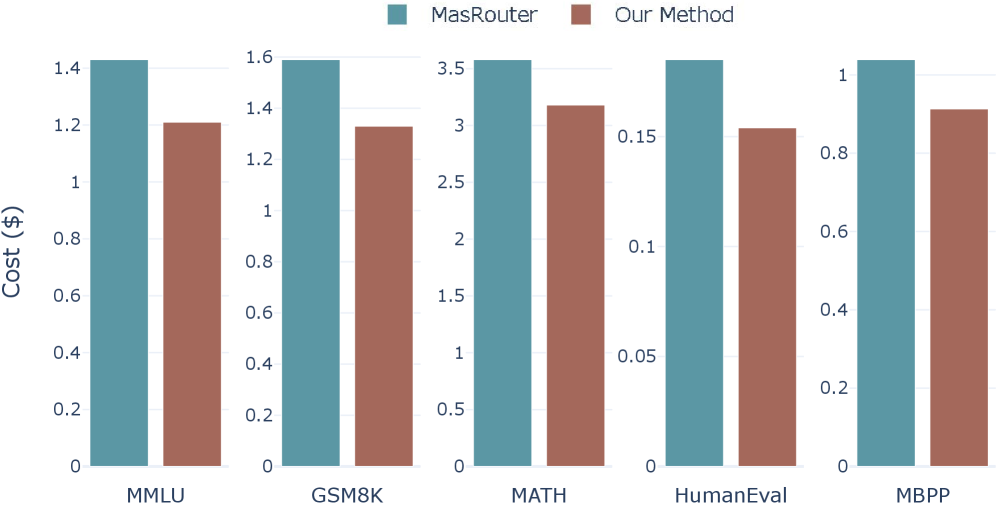
Fig 2: Figure 2: Comparison of inference costs between our work and MasRouter Yue et al. ( 2025 ) across various datasets.
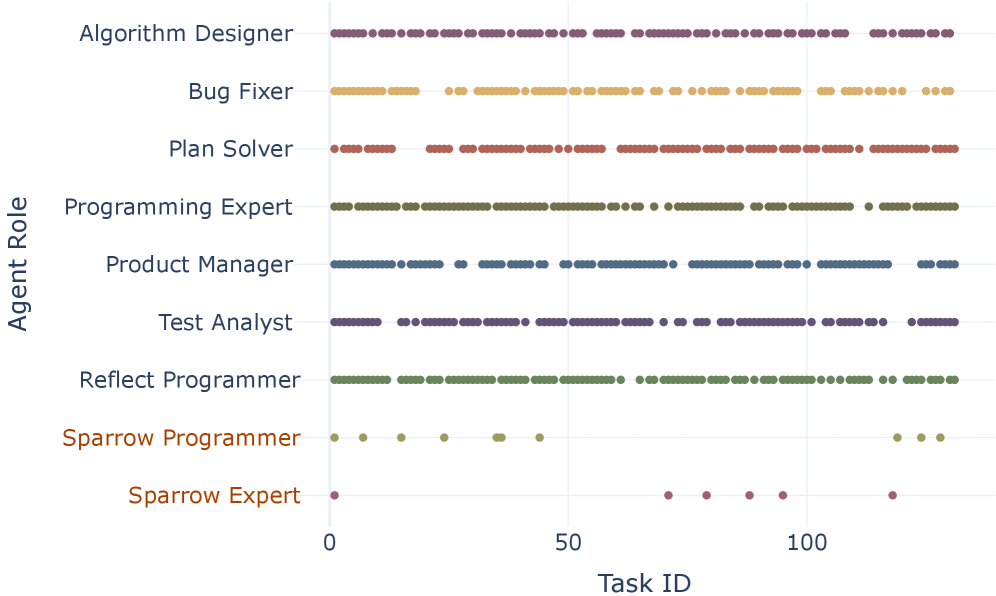
Fig 3: Figure 3: Distribution of roles chosen for reasoning on the HumanEval dataset, with the two roles beginning with Sparrow being the agents coded as error outputs.
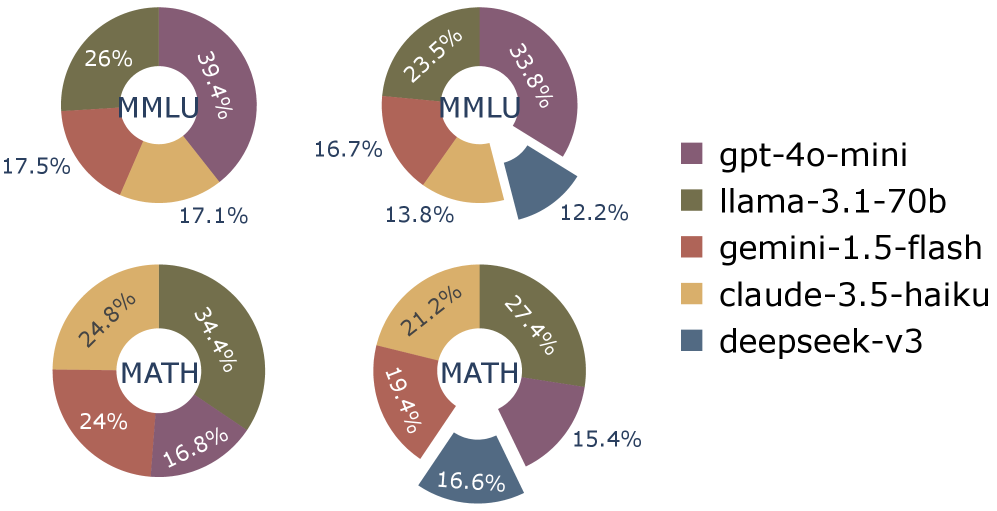
Fig 4: Figure 4: The selected LLM distribution of SC-MAS on MMLU and MATH.
Ready to evaluate your AI agents?
Learn how ReputAgent helps teams build trustworthy AI through systematic evaluation.
Learn MoreConsiderations
The system enforces a directed acyclic graph, so cyclic feedback loops or iterative mutual verification are not supported and could limit performance on some interactive tasks. Gains were measured on standard benchmarks (knowledge, math, code); real-world dialog-heavy or long-horizon tasks may behave differently. Practical deployment requires a heterogeneous pool of models and accurate cost measurements; joint optimization adds runtime and implementation complexity. This safety and policy guardrail approach is captured by the Guardrails Pattern.
Methodology & More
SC-MAS builds executable AI teams by combining three decisions for each input: which agent roles to include, how each selected pair of agents should interact, and which language model to run for each agent. Roles are chosen with a latent-variable selector that scores candidate roles given the query. Edge-level strategies (for example, critique, debate, or chain-of-thought) are explicitly represented on the graph edges so each interaction type is treated differently. Finally, a router assigns a model to each agent based on role and interaction context. The three modules are trained together to maximize a utility metric while penalizing token or compute cost, producing a directed acyclic graph that executes topologically to produce an answer. This approach is compatible with Semantic Capability Matching Pattern. On five benchmarks covering general knowledge, math reasoning, and code generation, the approach reduces token consumption by about 11–16% and improves accuracy by roughly 1.5–3.3% versus recent baselines. The main takeaway is that treating collaboration patterns between agents as first-class design choices, and jointly deciding who participates and what model they use, yields practical cost savings while slightly improving results. Future work should explore removing the acyclic constraint to allow iterative feedback, testing on long-running interactive tasks, and measuring end-to-end latency and orchestration overhead in production settings. Additionally, the design encourages explicit reasoning flows such as Chain of Thought Pattern.
Avoid common pitfallsLearn what failures to watch for
Credibility Assessment:
All authors have very low h-indexes and no affiliations or top-venue; limited signals of established expertise.